People will share misinformation that sparks “moral outrage”
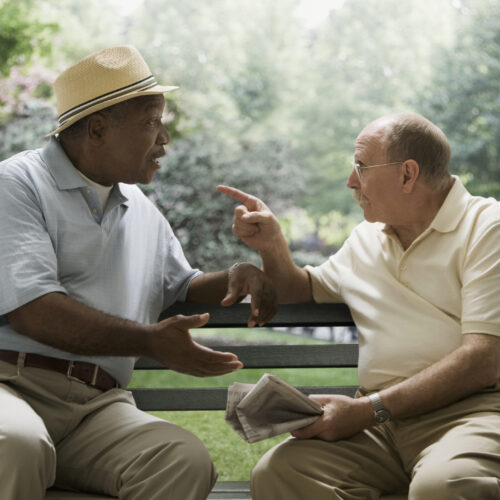
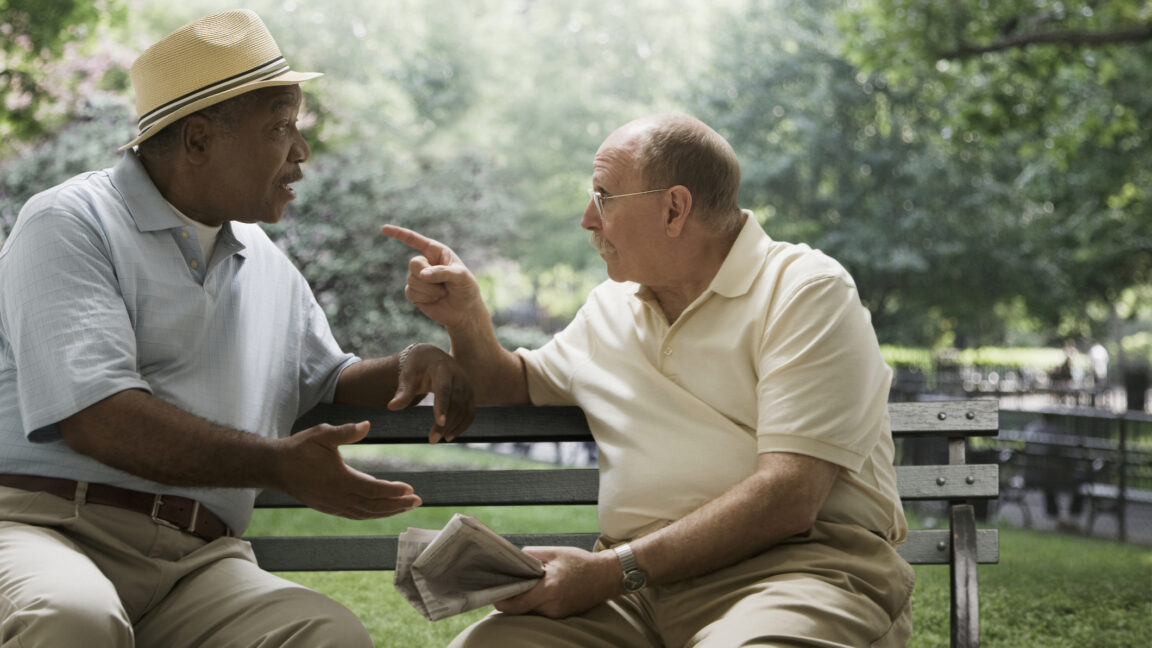
Rob Bauer, the chair of a NATO military committee, reportedly said, “It is more competent not to wait, but to hit launchers in Russia in case Russia attacks us. We must strike first.” These comments, supposedly made in 2024, were later interpreted as suggesting NATO should attempt a preemptive strike against Russia, an idea that lots of people found outrageously dangerous.
But lots of people also missed a thing about the quote: Bauer has never said it. It was made up. Despite that, the purported statement got nearly 250,000 views on X and was mindlessly spread further by the likes of Alex Jones.
Why do stories like this get so many views and shares? “The vast majority of misinformation studies assume people want to be accurate, but certain things distract them,” says William J. Brady, a researcher at Northwestern University. “Maybe it’s the social media environment. Maybe they’re not understanding the news, or the sources are confusing them. But what we found is that when content evokes outrage, people are consistently sharing it without even clicking into the article.” Brady co-authored a study on how misinformation exploits outrage to spread online. When we get outraged, the study suggests, we simply care way less if what’s got us outraged is even real.


© Ricardo Mendoza Garbayo