Amazon Taps Jennifer Hudson, Martha Stewart and More to Host Black Friday Shopping Shows Powered by TalkShopLive
















In recent years, materials scientists experimenting with ceramics have started adding an oxidized form of graphene to the mix to produce ceramics that are tougher, more durable, and more resistant to fracture, among other desirable properties. Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have developed a new method that uses ultrasound to more evenly distribute graphene oxide (GO) in ceramics, according to a new paper published in the journal ACS Omega. And as a bonus, they collaborated with an artist who used the resulting ceramic tiles to create a unique art exhibit at the NUS Museum—a striking merger of science and art.
As reported previously, graphene is the thinnest material yet known, composed of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. That structure gives it many unusual properties that hold great promise for real-world applications: batteries, super capacitors, antennas, water filters, transistors, solar cells, and touchscreens, just to name a few.
In 2021, scientists found that this wonder material might also provide a solution to the fading of colors of many artistic masterpieces. For instance, several of Georgia O'Keeffe's oil paintings housed in the Georgia O'Keeffe Museum in Santa Fe, New Mexico, have developed tiny pin-sized blisters, almost like acne, for decades. Conservators have found similar deterioration in oil-based masterpieces across all time periods, including works by Rembrandt.
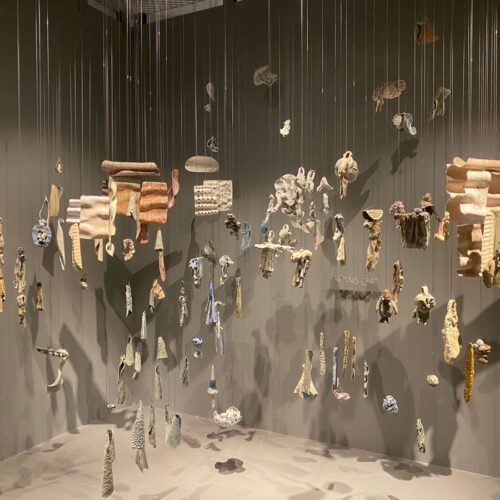
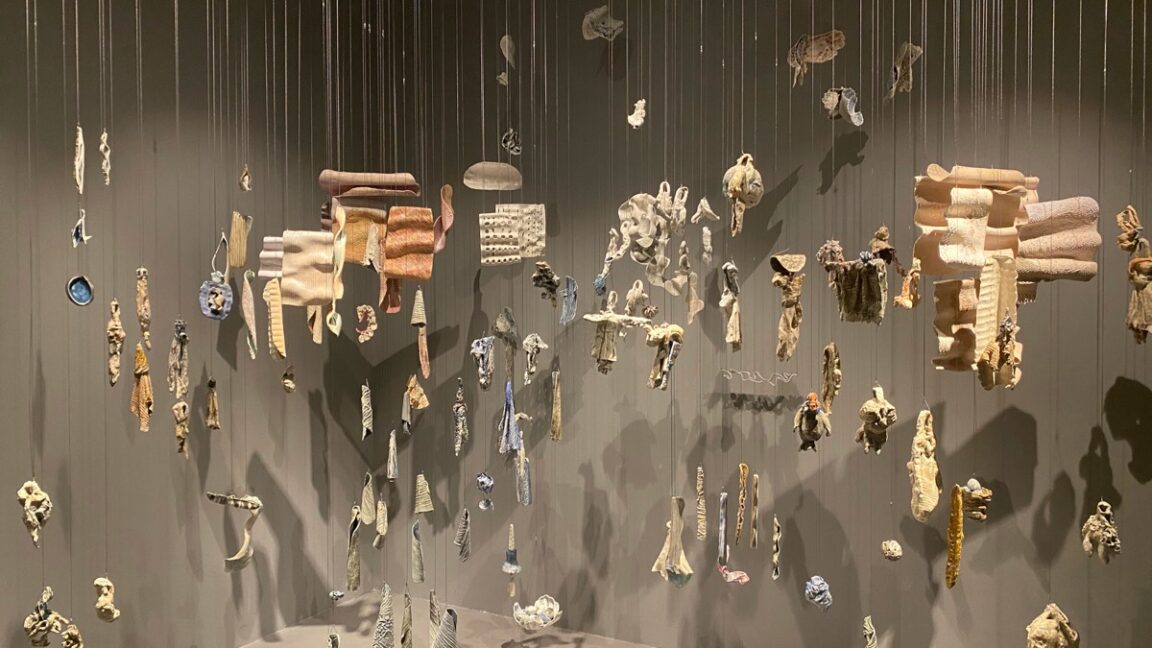


© Daria Andreeva and Delia Prvački.
Colossal, the company founded to try to restore the mammoth to the Arctic tundra, has also decided to tackle a number of other species that have gone extinct relatively recently: the dodo and the thylacine. Because of significant differences in biology, not the least of which is the generation time of Proboscideans, these other efforts may reach many critical milestones well in advance of the work on mammoths.
Late last week, Colossal released a progress report on the work involved in resurrecting the thylacine, also known as the Tasmanian tiger, which went extinct when the last known survivor died in a zoo in 1936. Marsupial biology has some features that may make de-extinction somewhat easier, but we have far less sophisticated ways of manipulating it compared to the technology we've developed for working with the stem cells and reproduction of placental mammals. But, based on these new announcements, the technology available for working with marsupials is expanding rapidly.
Colossal has branched out from its original de-extinction mission to include efforts to keep species from ever needing its services. In the case of marsupial predators, the de-extinction effort is incorporating work that will benefit existing marsupial predators: generating resistance to the toxins found on the cane toad, an invasive species that has spread widely across Australia.
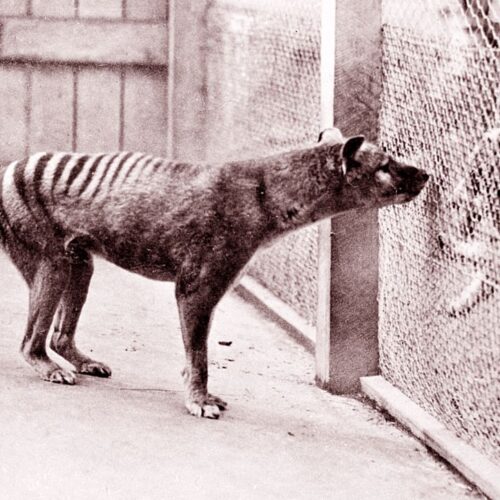
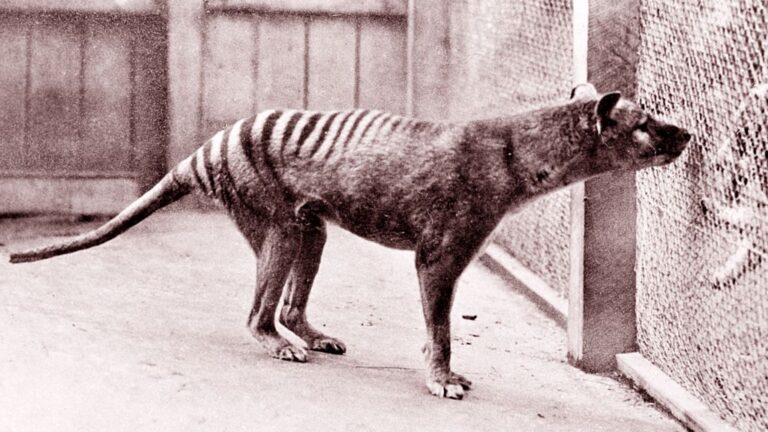


© Universal History Archive
A stunning image of differentiated mouse brain tumor cells has won the 2024 Nikon Small World photomicrography contest, yielding valuable insight into how degenerate diseases like Alzheimer's and ALS can arise from disruption in the cytoskeleton of brain cells. The image was taken by Bruno Cisterna, with assistance from Eric Vitriol, both with Augusta University in Georgia.
"One of the main problems with neurodegenerative diseases is that we don't fully understand what causes them,” Cisterna said in a statement. “To develop effective treatments, we need to figure out the basics first. Our research is crucial for uncovering this knowledge and ultimately finding a cure. Differentiated cells could be used to study how mutations or toxic proteins that cause Alzheimer's or ALS alter neuronal morphology, as well as to screen potential drugs or gene therapies aimed at protecting neurons or restoring their function.”
It's the 50th anniversary of Nikon's annual contest, which was founded back in 1974 "to showcase the beauty and complexity of things seen through the light microscope." Photomicrography involves attaching a camera to a microscope (either an optical microscope or an electron microscope) so that the user can take photographs of objects at very high resolutions. British physiologist Richard Hill Norris was one of the first to use it for his studies of blood cells in 1850, and the method has increasingly been highlighted as art since the 1970s. There have been many groundbreaking technological advances in the ensuing decades, particularly with the advent of digital imaging methods.
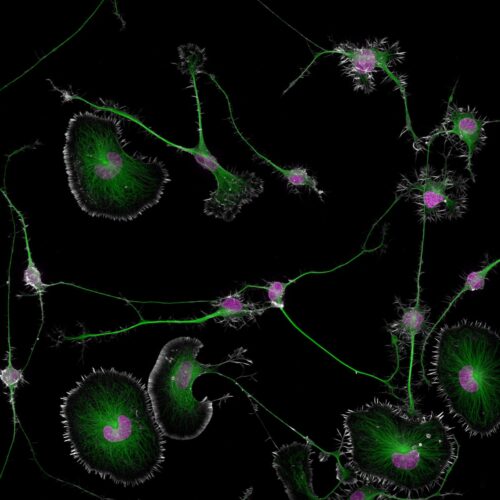
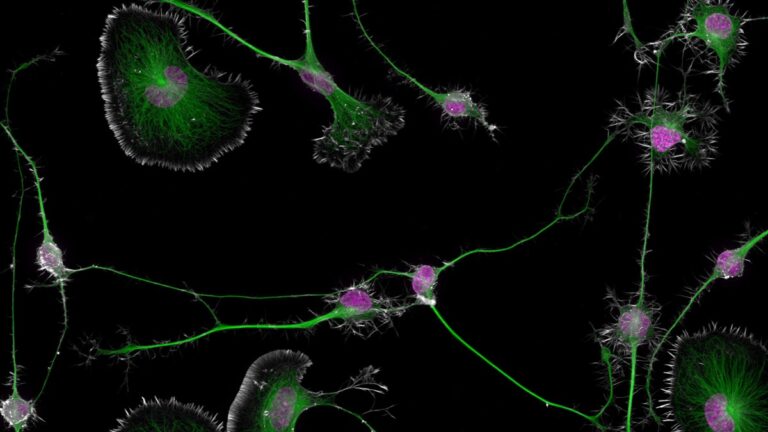
© Bruno Cisterna & Eric Vitrol/Nikon Small World
Two years ago, a NASA spacecraft smashed into a small asteroid millions of miles from Earth to test a technique that could one day prove useful to deflect an object off a collision course with Earth. The European Space Agency launched a follow-up mission Monday to go back to the crash site and see the damage done.
The nearly $400 million (363 million euro) Hera mission, named for the Greek goddess of marriage, will investigate the aftermath of a cosmic collision between NASA's DART spacecraft and the skyscraper-size asteroid Dimorphos on September 26, 2022. NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test mission was the first planetary defense experiment, and it worked, successfully nudging Dimorphos off its regular orbit around a larger companion asteroid named Didymos.
But NASA had to sacrifice the DART spacecraft in the deflection experiment. Its destruction meant there were no detailed images of the condition of the target asteroid after the impact. A small Italian CubeSat deployed by DART as it approached Dimorphos captured fuzzy long-range views of the collision, but Hera will perform a comprehensive survey when it arrives in late 2026.


© SpaceX
Paper quilling, also known as filigree, is a captivating paper craft technique that involves rolling, shaping, and gluing strips of paper to create intricate and beautiful designs. Whether you’re a seasoned crafter or a beginner, DIY paper quilling offers endless possibilities for creativity and self-expression. This art form is easy to learn, requires minimal materials, and can be used to…
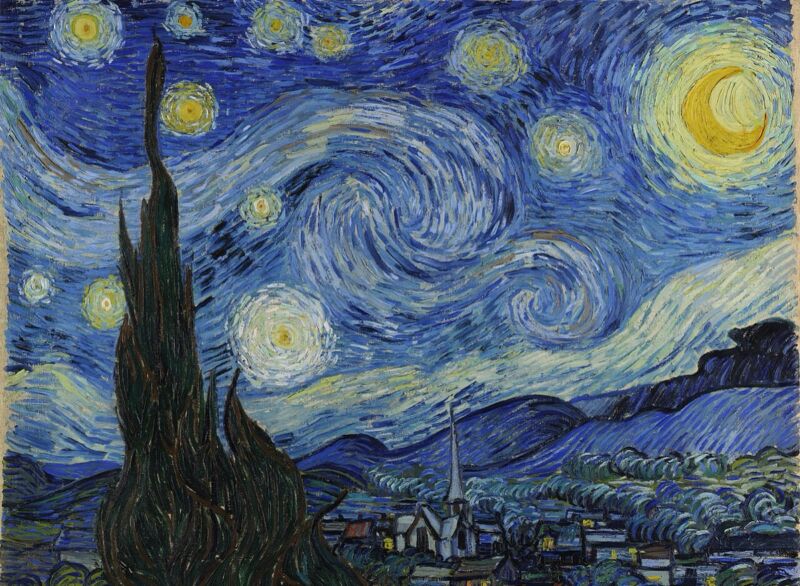

Enlarge / Many have seen a reflection of Vincent van Gogh's inner turmoil in the swirling vortices of The Starry Night. (credit: Public doman)
Vincent van Gogh's most famous painting is The Starry Night (1889), created (along with several other masterpieces) during the artist's stay at an asylum in Arles following his breakdown in December 1888. Where some have seen the swirling vortices of the night sky depicted in Starry Night as a reflection of van Gogh's own inner turmoil, physicists often see a masterful depiction of atmospheric turbulence. According to a new paper published in the journal Physics of Fluids, the illusion of movement in van Gogh's blue sky is also due to the scale of the paint strokes—a second kind of "hidden turbulence" at the microscale that diffuses throughout the entire canvas.
“It reveals a deep and intuitive understanding of natural phenomena,” said co-author Yongxiang Huang of Xiamen University in China. “Van Gogh’s precise representation of turbulence might be from studying the movement of clouds and the atmosphere or an innate sense of how to capture the dynamism of the sky.”
Physicists have long been fascinated by van Gogh's innate feel for turbulence. As previously reported, in a 2014 TED-Ed talk, Natalya St. Clair, a research associate at the Concord Consortium and coauthor of The Art of Mental Calculation, used Starry Night to illuminate the concept of turbulence in a flowing fluid. In particular, she talked about how van Gogh's technique allowed him (and other Impressionist painters) to represent the movement of light across water or in the twinkling of stars. We see this as a kind of shimmering effect, because the eye is more sensitive to changes in the intensity of light (a property called luminance) than to changes in color.
Food styling is an essential aspect of the culinary world, transforming ordinary dishes into visually stunning works of art. This practice involves arranging food in an aesthetically pleasing manner to enhance its appeal for photography, media, and presentation. As an expert in Food and Cooking, I will explore the fundamentals of food styling, share valuable tips and techniques…