Routine dental X-rays are not backed by evidence—experts want it to stop
Has your dentist ever told you that it's recommended to get routine dental X-rays every year? My (former) dentist's office did this year—in writing, even. And they claimed that the recommendation came from the American Dental Association.
It's a common refrain from dentists, but it's false. The American Dental Association does not recommend annual routine X-rays. And this is not new; it's been that way for well over a decade.
The association's guidelines from 2012 recommended that adults who don't have an increased risk of dental caries (myself included) need only bitewing X-rays of the back teeth every two to three years. Even people with a higher risk of caries can go as long as 18 months between bitewings. The guidelines also note that X-rays should not be preemptively used to look for problems: "Radiographic screening for the purpose of detecting disease before clinical examination should not be performed," the guidelines read. In other words, dentists are supposed to examine your teeth before they take any X-rays.
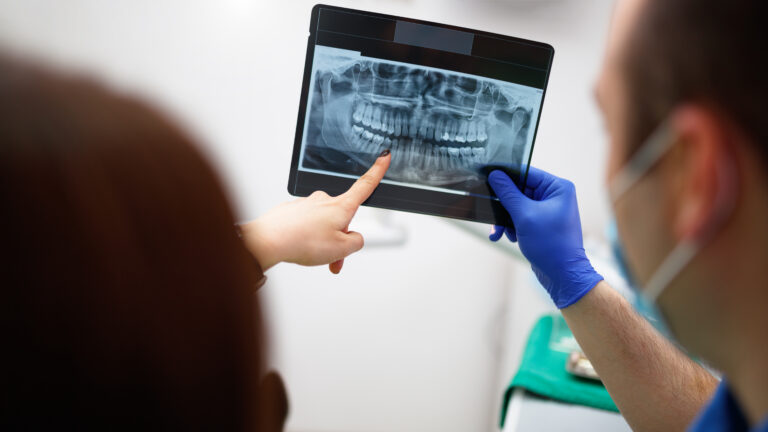
© Getty | MilanEXPO