As hospitals struggle with IV fluid shortage, NC plant restarts production
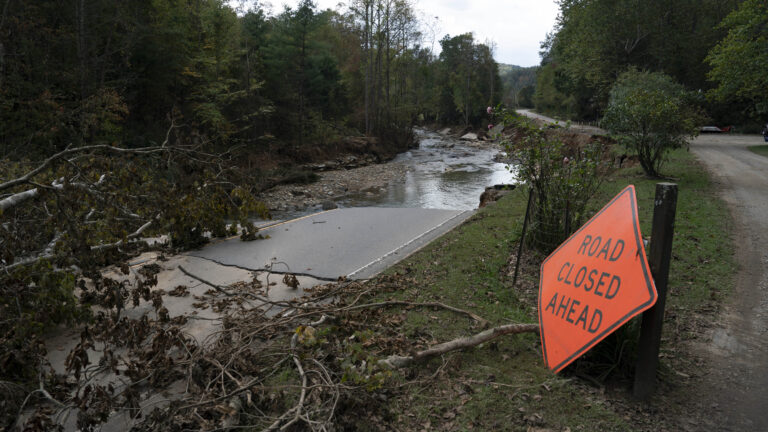
The western North Carolina plant that makes 60 percent of the country's intravenous fluid supply has restarted its highest-producing manufacturing line after being ravaged by flooding brought by Hurricane Helene last month.
While it's an encouraging sign of recovery as hospitals nationwide struggle with shortages of fluids, supply is still likely to remain tight for the coming weeks.
IV fluid-maker Baxter Inc, which runs the Marion plant inundated by Helene, said Thursday that the restarted production line could produce, at peak, 25 percent of the plant's total production and about 50 percent of the plant's production of one-liter IV solutions, the product most commonly used by hospitals and clinics.
© Getty | The Washington Post







