Homeopathic company refuses to recall life-threatening nasal spray, FDA says
Enlarge (credit: Getty | Florian Gaertner)
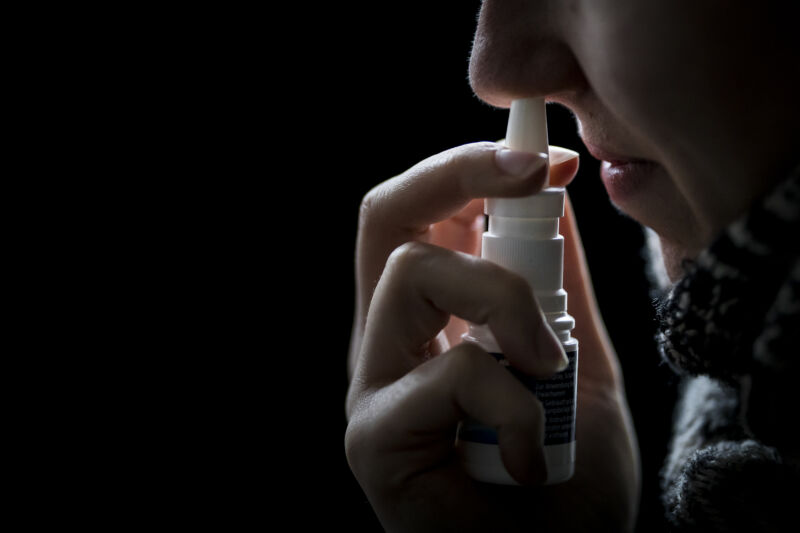
The maker of a homeopathic nasal spray with a history of contamination is refusing to recall its product after the Food and Drug Administration once again found evidence of dangerous microbial contamination.
In a warning Thursday, the FDA advised consumers to immediately stop using SnoreStop nasal spray—made by Green Pharmaceuticals—because it may contain microbes that, when sprayed directly into nasal cavities, can cause life-threatening infections. The FDA highlighted the risk to people with compromised immune systems and also children, since SnoreStop is marketed to kids as young as age 5.
According to the regulator, an FDA inspection in April uncovered laboratory test results showing that a batch of SnoreStop contained "significant microbial contamination." But, instead of discarding the batch, FDA inspectors found evidence that Green Pharmaceuticals had repackaged some of the contaminated lot and distributed it as single spray bottles or as part of a starter kit.