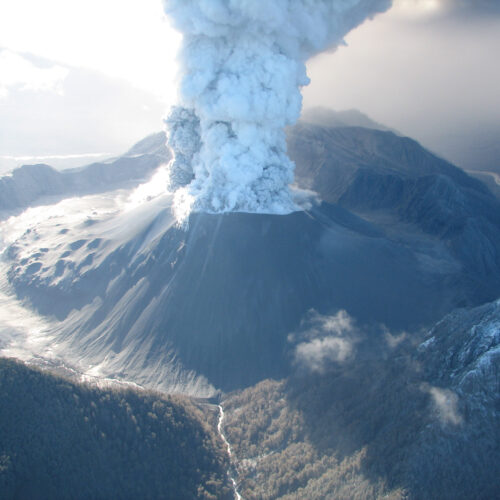
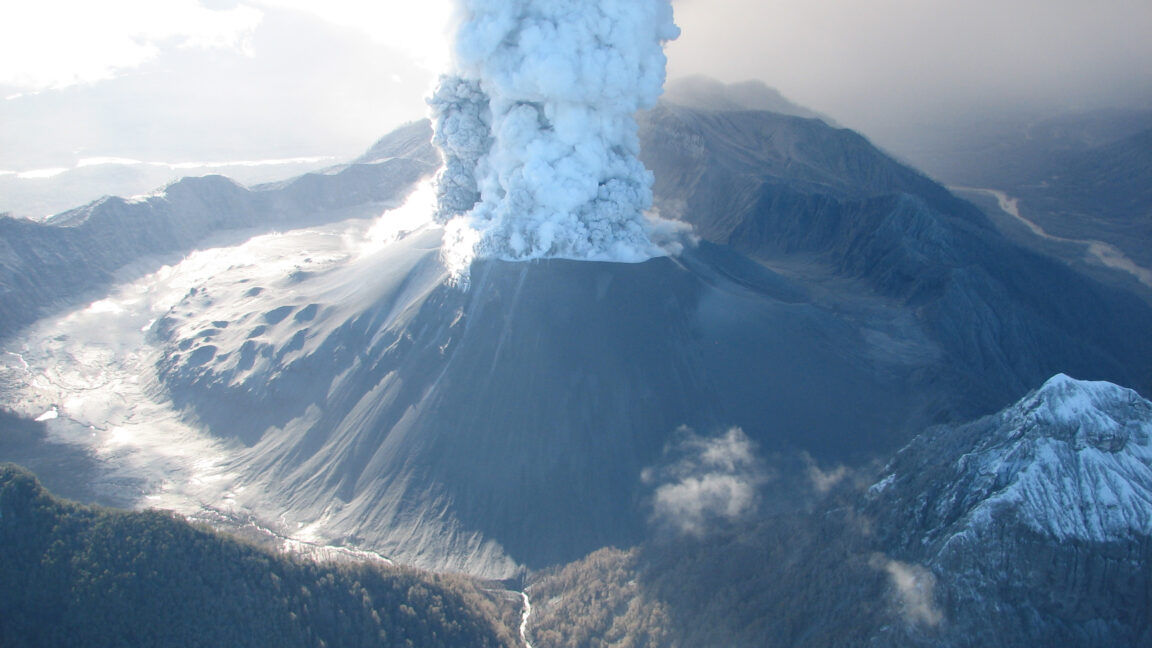
One less thing to worry about in 2025: Yellowstone probably won’t go boom
It's difficult to comprehend what 1,000 cubic kilometers of rock would look like. It's even more difficult to imagine it being violently flung into the air. Yet the Yellowstone volcanic system blasted more than twice that amount of rock into the sky about 2 million years ago, and it has generated a number of massive (if somewhat smaller) eruptions since, and there have been even larger eruptions deeper in the past.
All of which might be enough to keep someone nervously watching the seismometers scattered throughout the area. But a new study suggests that there's nothing to worry about in the near future: There's not enough molten material pooled in one place to trigger the sort of violent eruptions that have caused massive disruptions in the past. The study also suggests that the primary focus of activity may be shifting outside of the caldera formed by past eruptions.
Understanding Yellowstone
Yellowstone is fueled by what's known as a hotspot, where molten material from the Earth's mantle percolates up through the crust. The rock that comes up through the crust is typically basaltic (a definition based on the ratio of elements in its composition) and can erupt directly. This tends to produce relatively gentle eruptions where lava flows across a broad area, generally like you see in Hawaii and Iceland. But this hot material can also melt rock within the crust, producing a material called rhyolite. This is a much more viscous material that does not flow very readily and, instead, can cause explosive eruptions.


© Deb Snelson











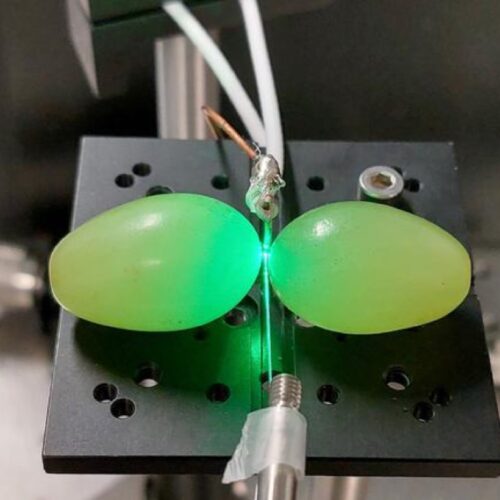
 An experiment with experienced fighters who spar freely using different styles.
Credit:
An experiment with experienced fighters who spar freely using different styles.
Credit:













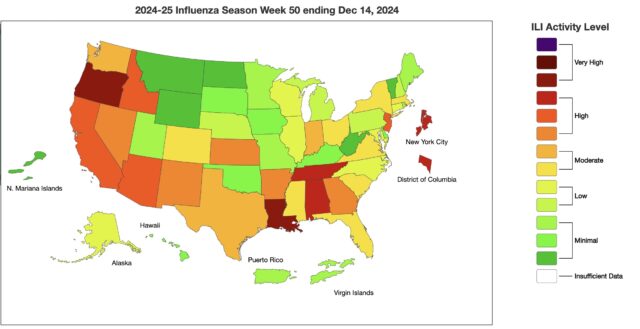 Map of ILI activity by state
Credit:
Map of ILI activity by state
Credit:
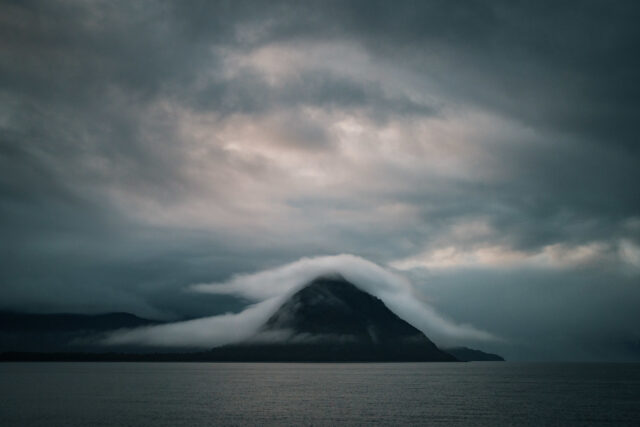



 Mists shroud the hillsides at the entrance to Chaitén Bay, as seen from aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s <em>Falkor (too)</em> research vessel.
Credit:
Alex Ingle / Schmidt Ocean Institute
Mists shroud the hillsides at the entrance to Chaitén Bay, as seen from aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s <em>Falkor (too)</em> research vessel.
Credit:
Alex Ingle / Schmidt Ocean Institute

