Could microwaved grapes be used for quantum sensing?
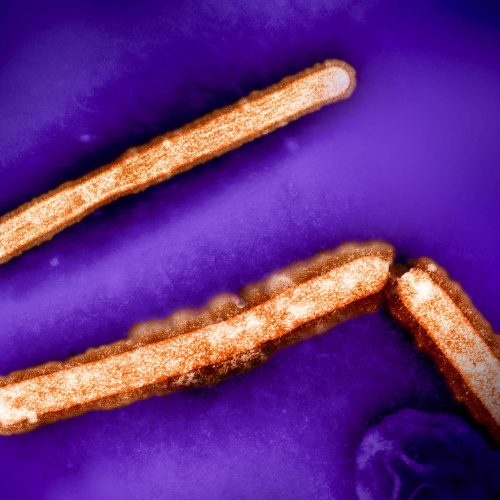
There are thousands of YouTube videos in which DIY science enthusiasts cut grapes in half—leaving just a thin bit of skin connecting them—and put the grapes in the microwave, just to marvel at the sparks and plume of ionized gas (plasma) that the grapes produce. This quirky property of grapes might help make more efficient quantum sensors, according to a new paper published in the journal Physical Review Applied.
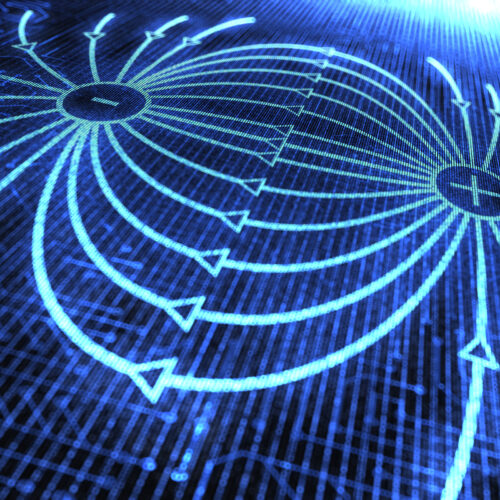
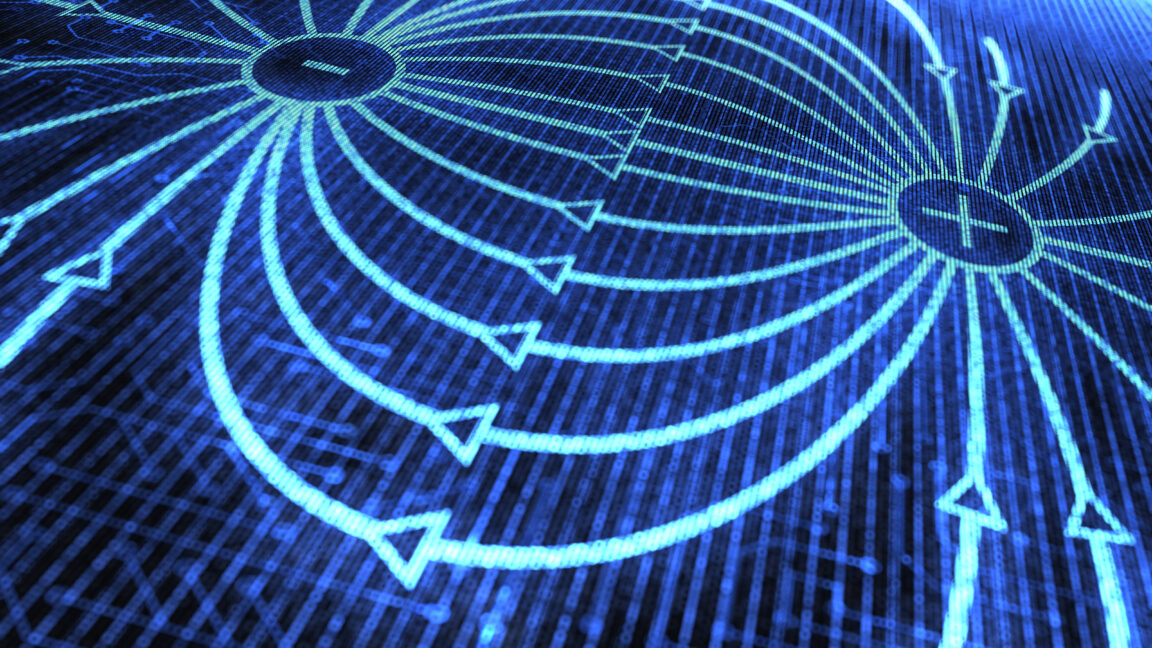
The plasma-inducing grape effect was first observed in 1994, per the authors. As previously reported, the usual explanation for the generation of plasmas is that grapes are so small that the irradiating microwaves become highly concentrated in the grape tissue, ripping some the molecules apart to generate charged ions (adding to the electrolytes already present in the grapes). The electromagnetic field that forms causes ions to flow from one grape half to the other via the connecting skin—at least at first. That's when you get the initial sparks. Eventually, the ions start passing through the surrounding air as well, ionizing it to produce that hot plume of plasma.
But in 2019, Trent University scientists showed that explanation isn't quite right. The skin bridge isn't necessary for the effect to occur. Rather, the plasma is generated by an electromagnetic "hot spot." The grapes have the right refractive index and size to "trap" microwaves, so putting two of them close together leads to the generation of a hot spot between them. The trick also works with gooseberries, large blackberries, and quail eggs, as well as hydrogel beads—plastic beads soaked in water. ("Many microwaves were in fact harmed during the experiments," co-author Hamza Khattak admitted at the time.)
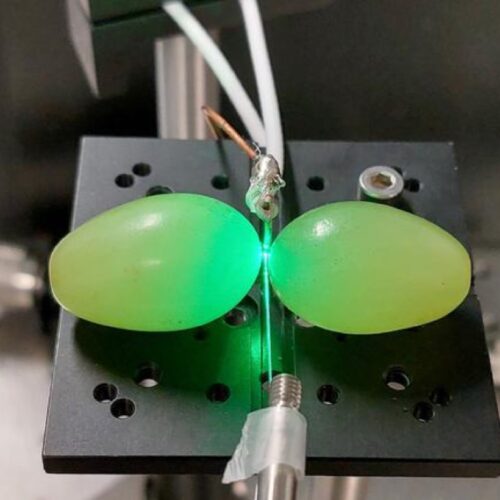
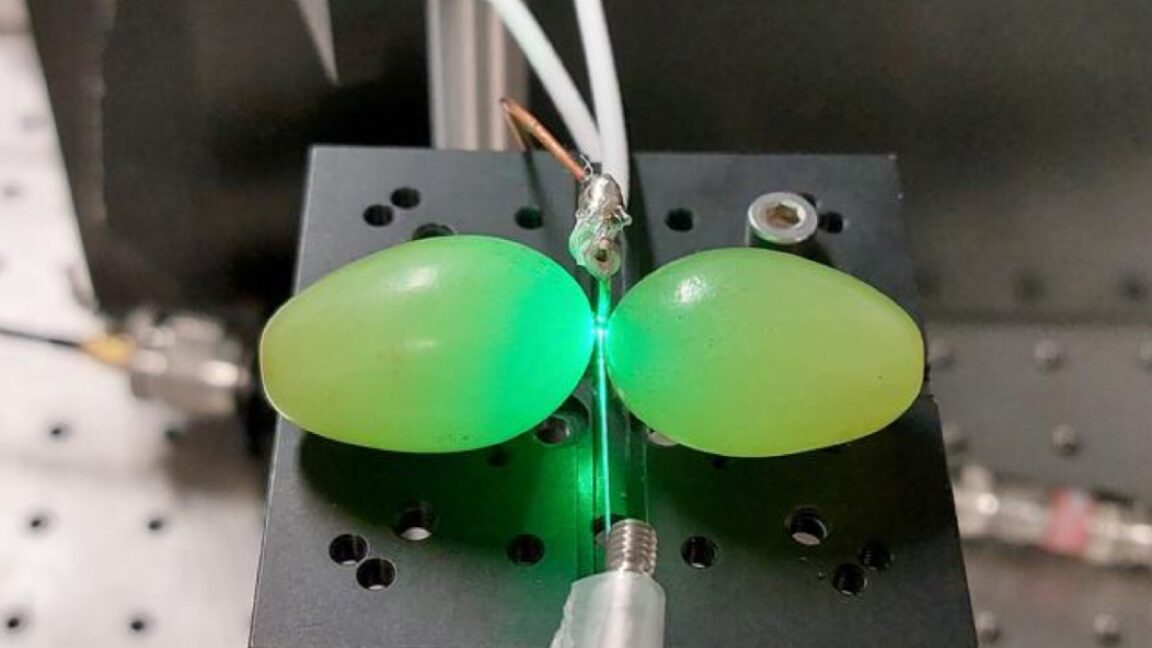
© Fawaz, Nair, Volz




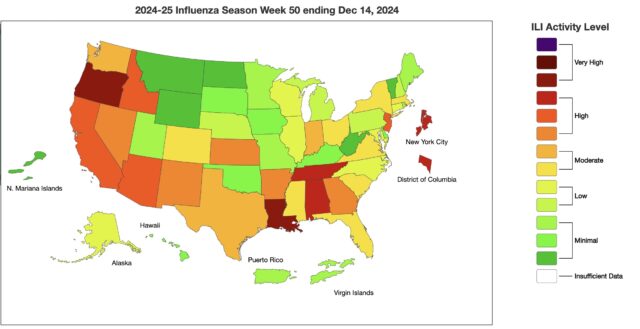 Map of ILI activity by state
Credit:
Map of ILI activity by state
Credit:
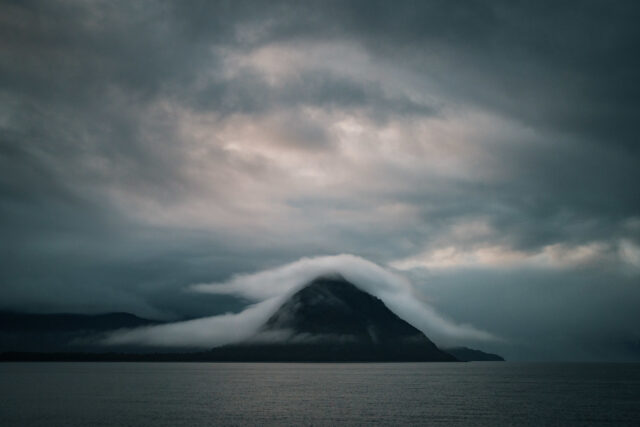



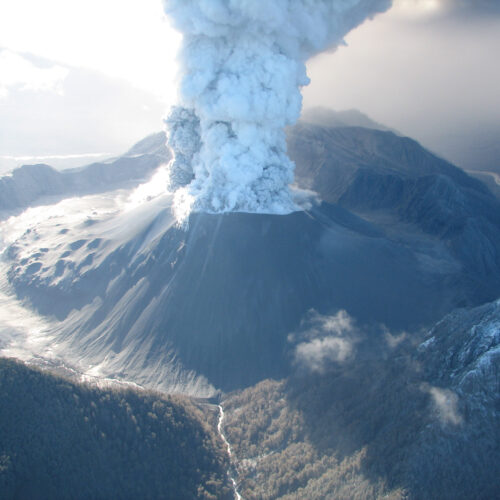
 Mists shroud the hillsides at the entrance to Chaitén Bay, as seen from aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s <em>Falkor (too)</em> research vessel.
Credit:
Alex Ingle / Schmidt Ocean Institute
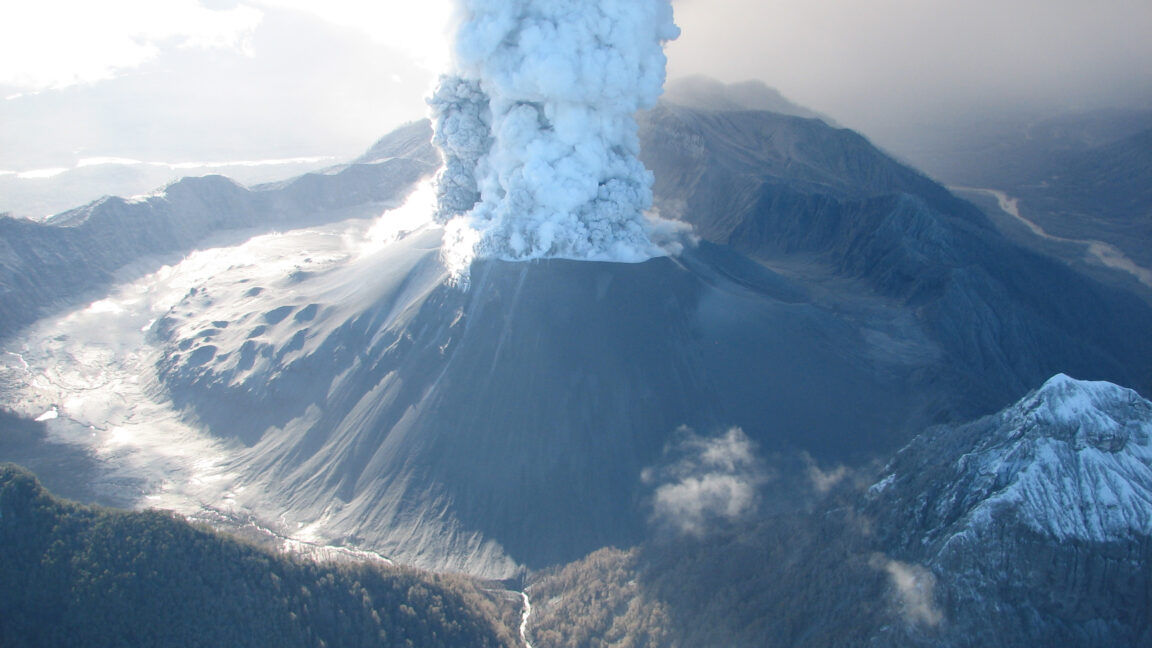
Mists shroud the hillsides at the entrance to Chaitén Bay, as seen from aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s <em>Falkor (too)</em> research vessel.
Credit:
Alex Ingle / Schmidt Ocean Institute