Researchers use AI to design proteins that block snake venom toxins
It has been a few years since AI began successfully tackling the challenge of predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins, complex molecules that are essential for all life. Next-generation tools are now available, and the Nobel Prizes have been handed out. But people not involved in biology can be forgiven for asking whether any of it can actually make a difference.
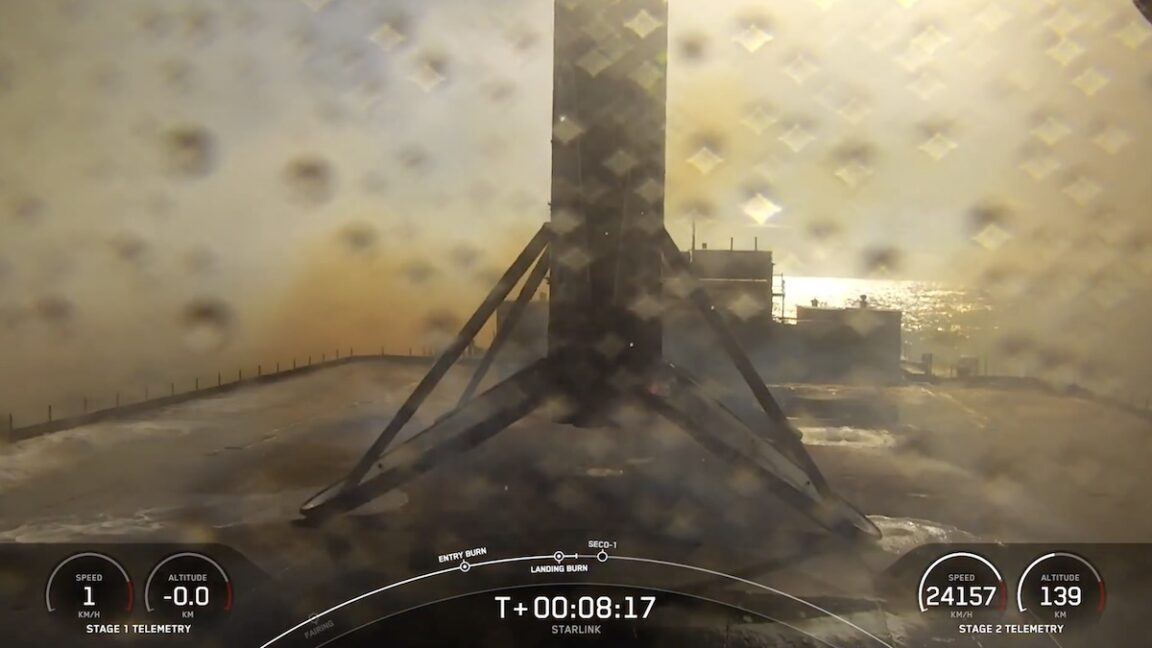
A nice example of how the tools can be put to use is being released in Nature on Wednesday. A team that includes the University of Washington's David Baker, who picked up his Nobel in Stockholm last month, used software tools to design completely new proteins that are able to inhibit some of the toxins in snake venom. While not entirely successful, the work shows how the new software tools can let researchers tackle challenges that would otherwise be difficult or impossible.
Blocking venom
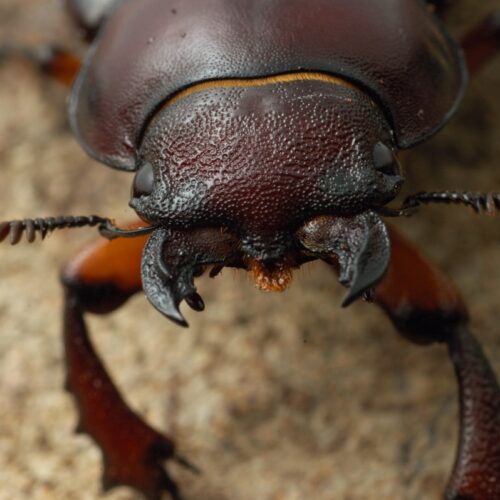
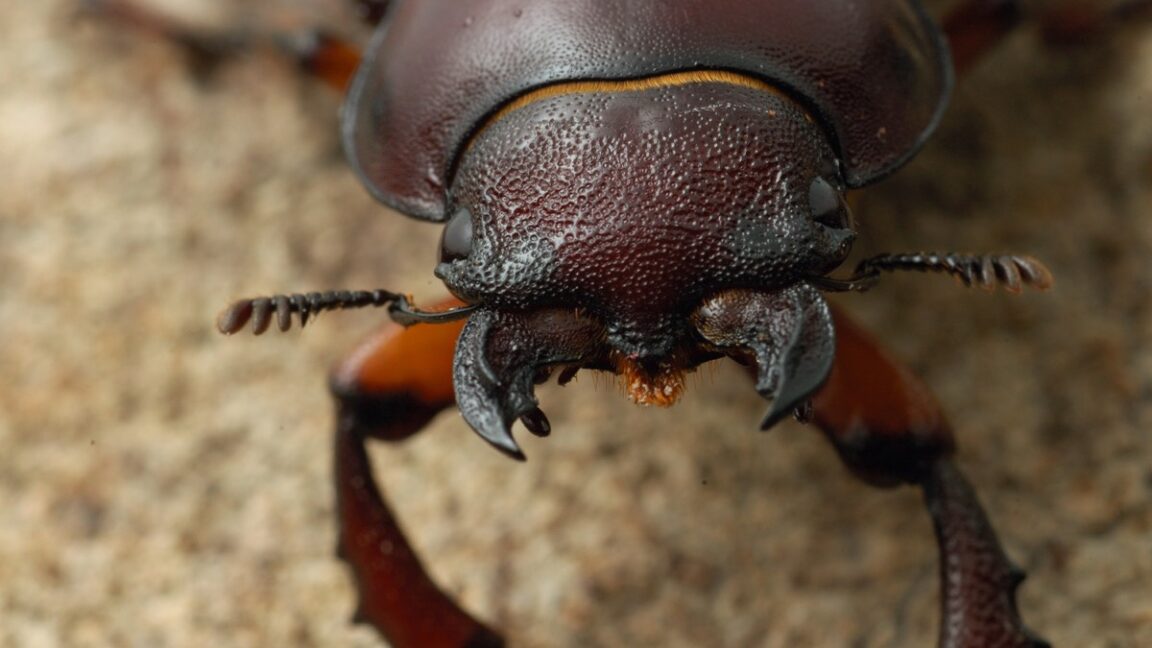
Snake venom includes a complicated mix of toxins, most of them proteins, that engage in a multi-front assault on anything unfortunate enough to get bitten. Right now, the primary treatment is to use a mix of antibodies that bind to these toxins, produced by injecting sub-lethal amounts of venom proteins into animals. But antivenon treatments tend to require refrigeration, and even then, they have a short shelf life. Ensuring a steady supply also means regularly injecting new animals and purifying more antibodies from them.


© Paul Starosta






























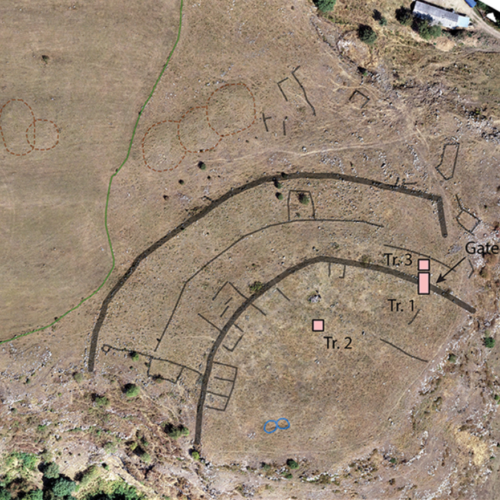
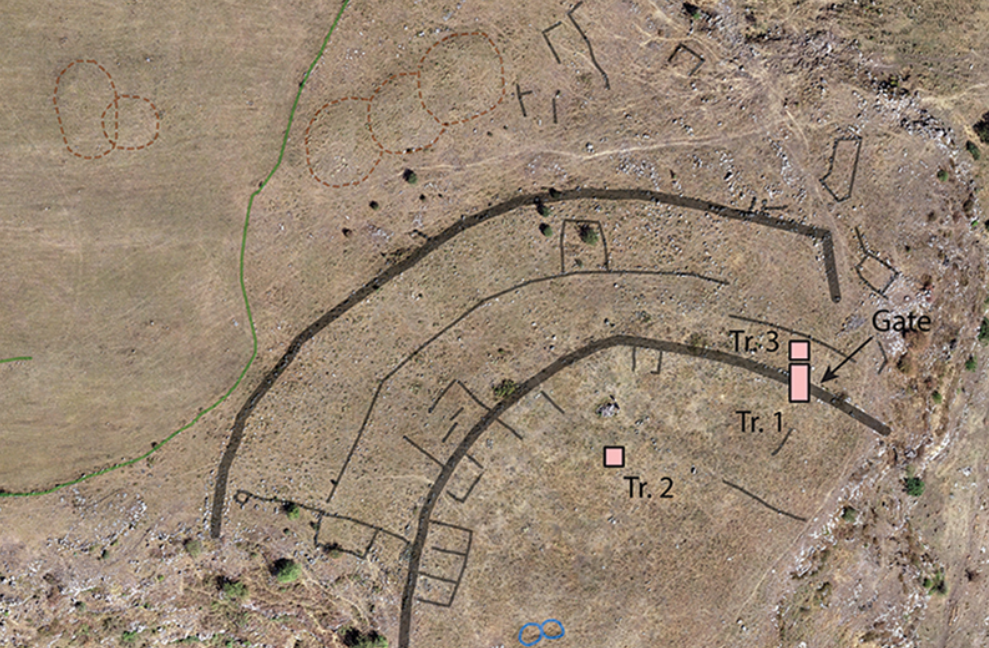
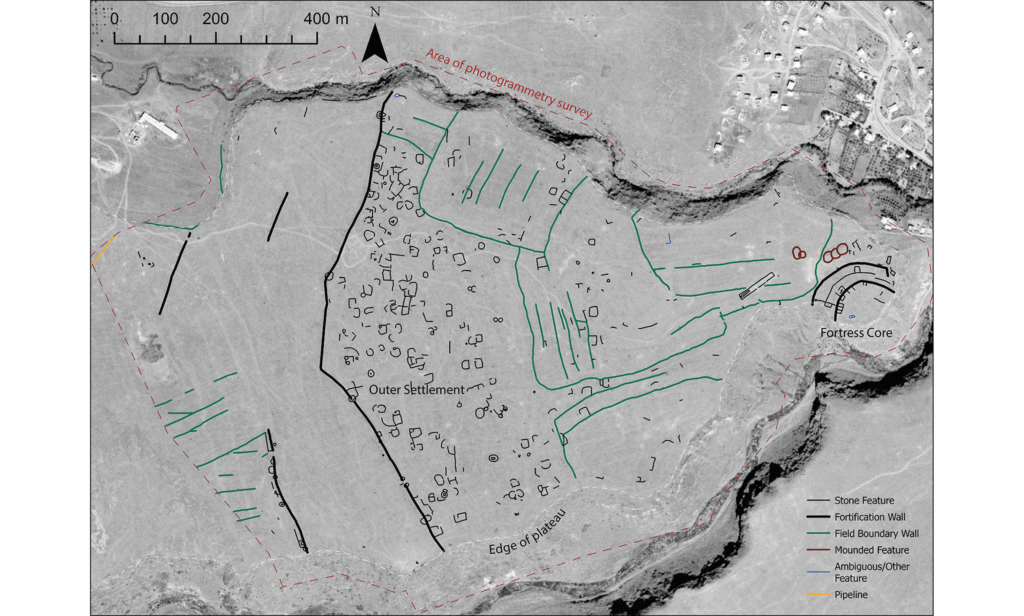 This map shows an aerial map of the ancient megafortress at Dmanisis Gora.
Credit:
Erb-Satullo et al. 2025
This map shows an aerial map of the ancient megafortress at Dmanisis Gora.
Credit:
Erb-Satullo et al. 2025