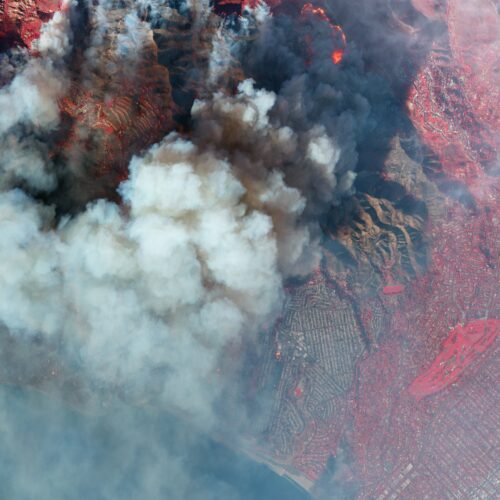
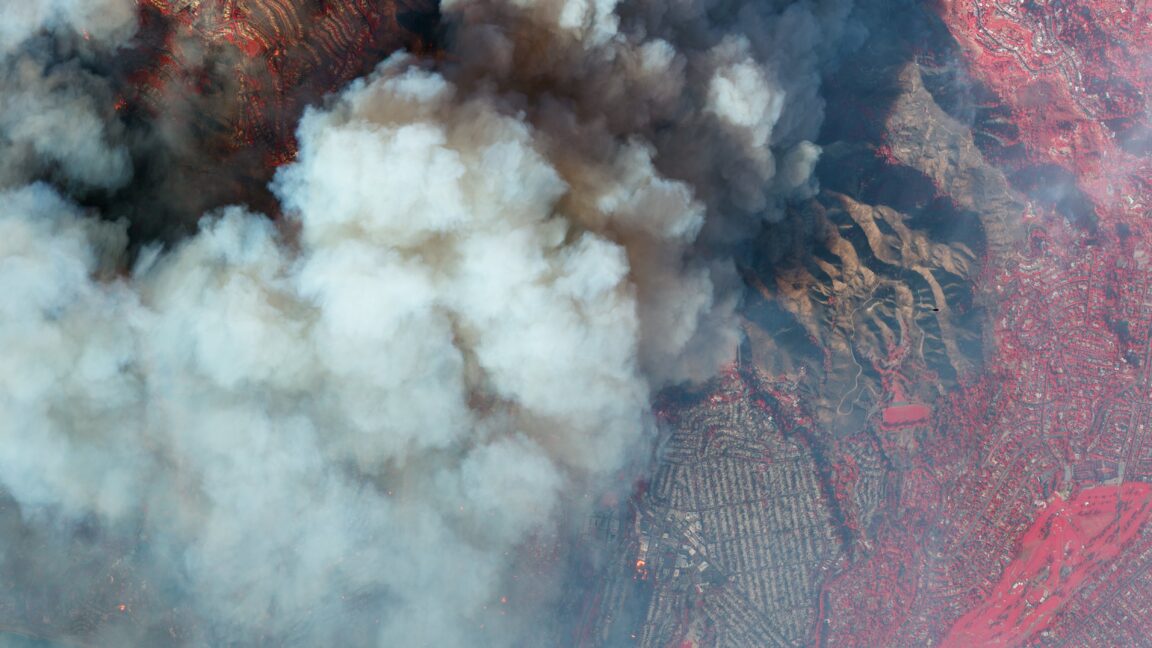
How to get a perfect salt ring deposit in your pasta pot
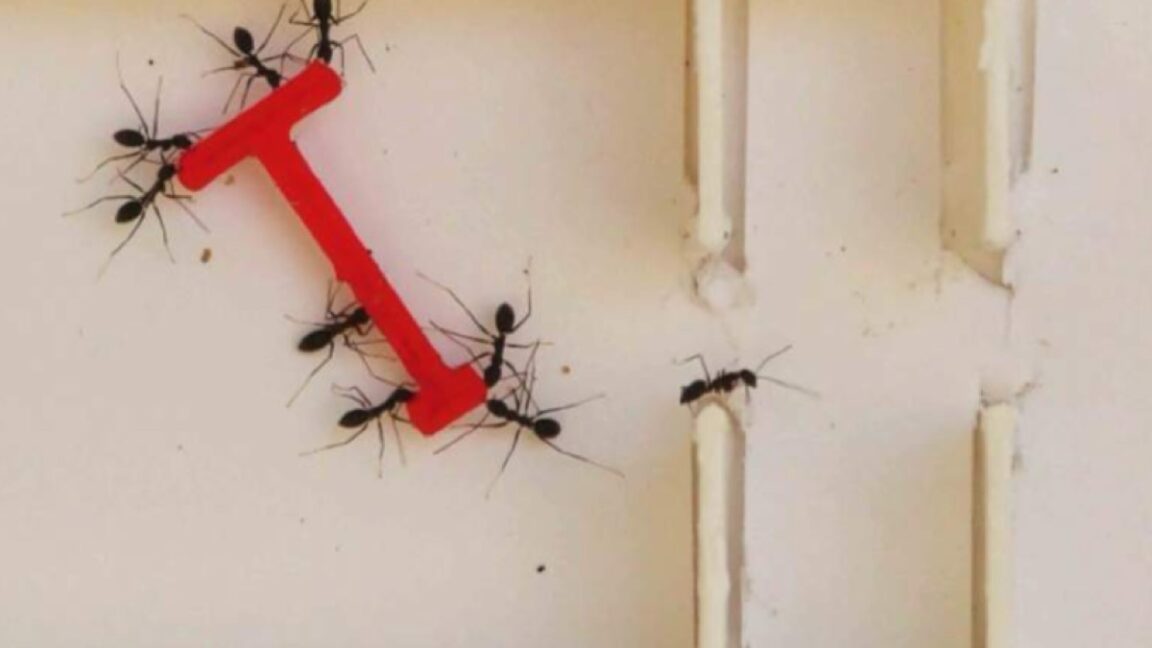
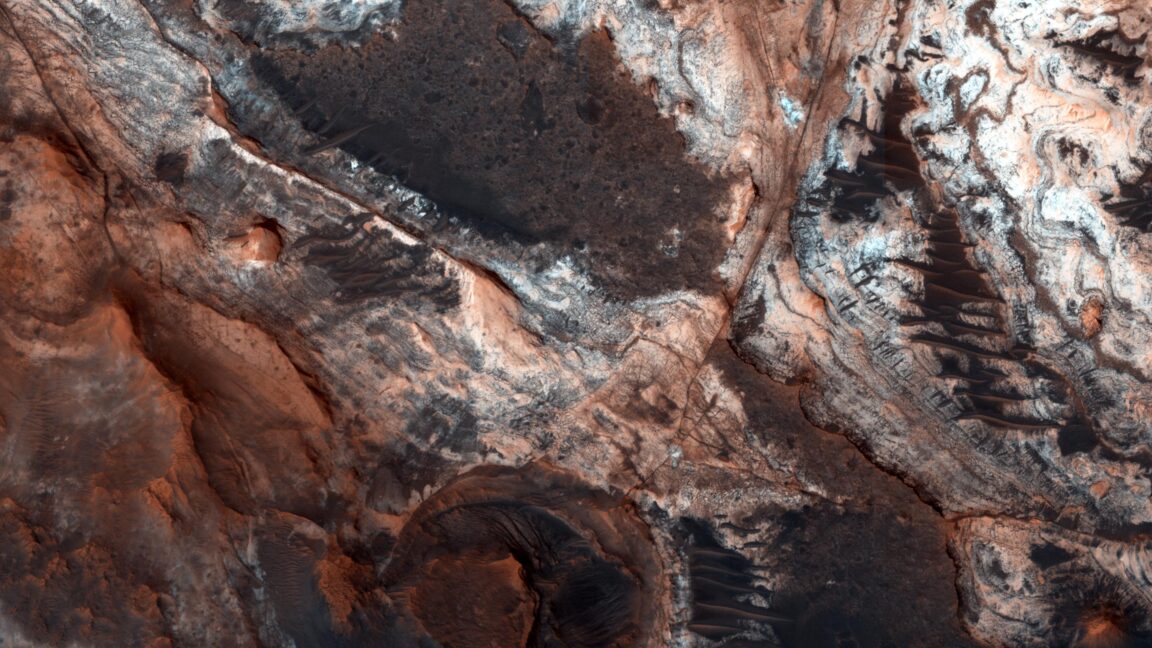
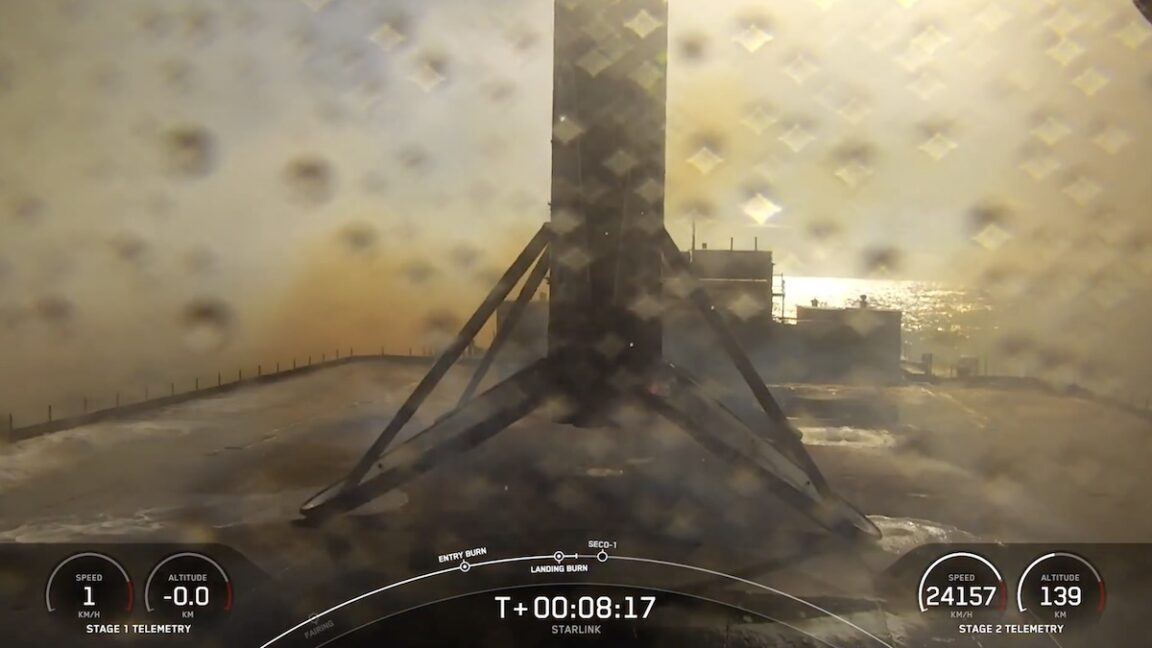
Physicist Mathieu Souzy of the University Twente was enjoying an evening of pasta and board games with several colleagues when the conversation turned to how adding salt to a pasta pot to make it boil faster can leave a white ring on the bottom of the pot. Ever the curious scientists, they wondered about the various factors that would contribute to creating the perfect circular pattern for a salt ring.
“By the end of our meal, we’d sketched an experimental protocol and written a succession of experiments we wanted to try on my youngest son’s small whiteboard,” said Souzy. It all comes down to three factors: the diameter of the particles (grains of salt, in this case), the settling height, and the number of particles released simultaneously, according to a new paper published in the journal Physics of Fluids.
We've previously reported on physicists' longstanding interest in similar phenomena like the "coffee ring effect," when a single liquid evaporates and the solids that had been dissolved in the liquid (like coffee grounds) form a ring. It happens because the evaporation occurs faster at the edge than at the center. Any remaining liquid flows outward to the edge to fill in the gaps, dragging those solids with it. Mixing in solvents (water or alcohol) reduces the effect as long as the drops are very small. Large drops produce more uniform stains.
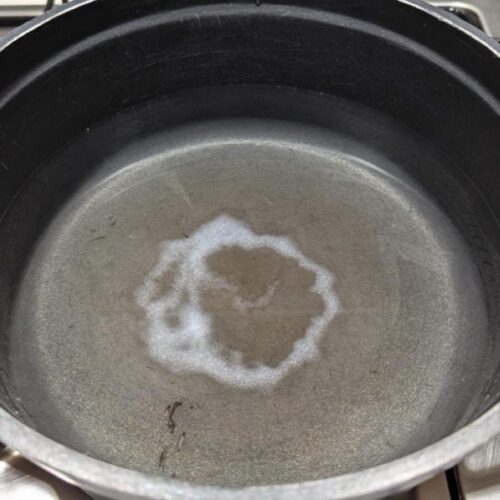
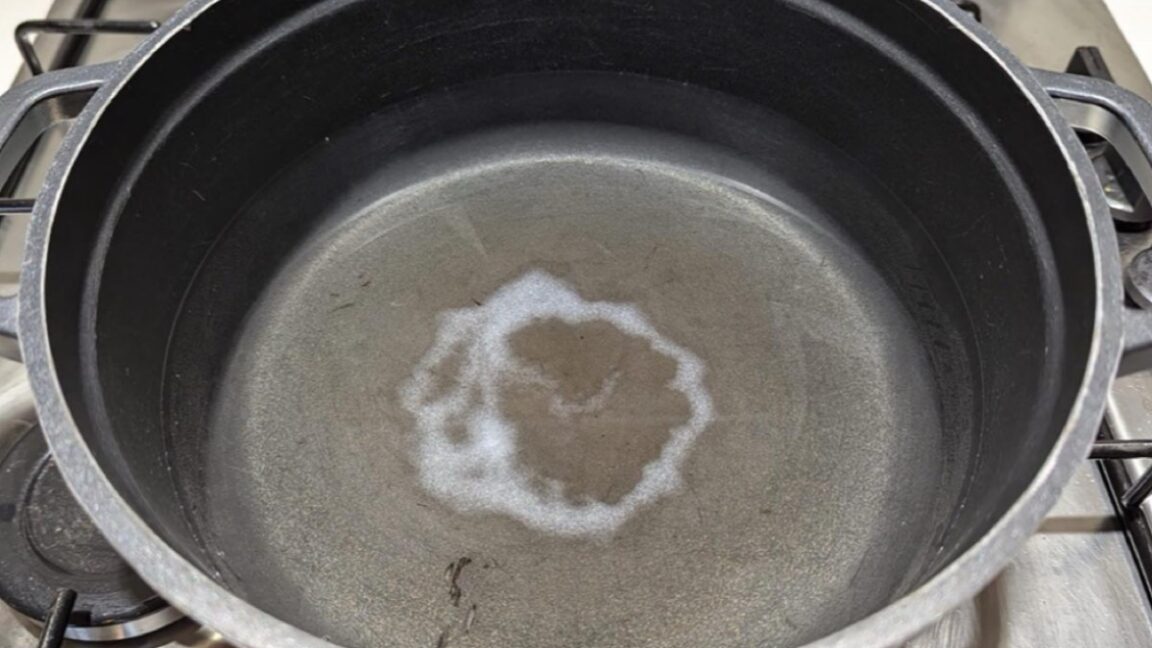


© Mathieu Souzy












































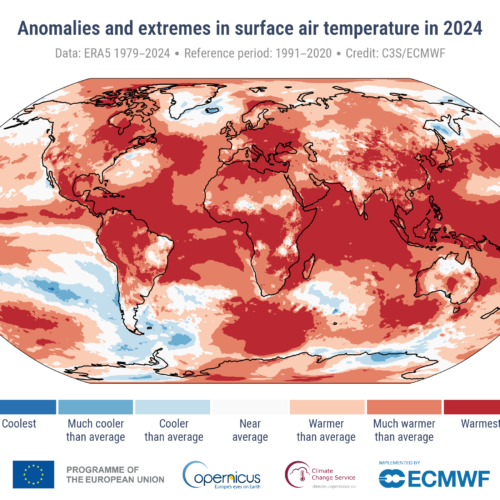
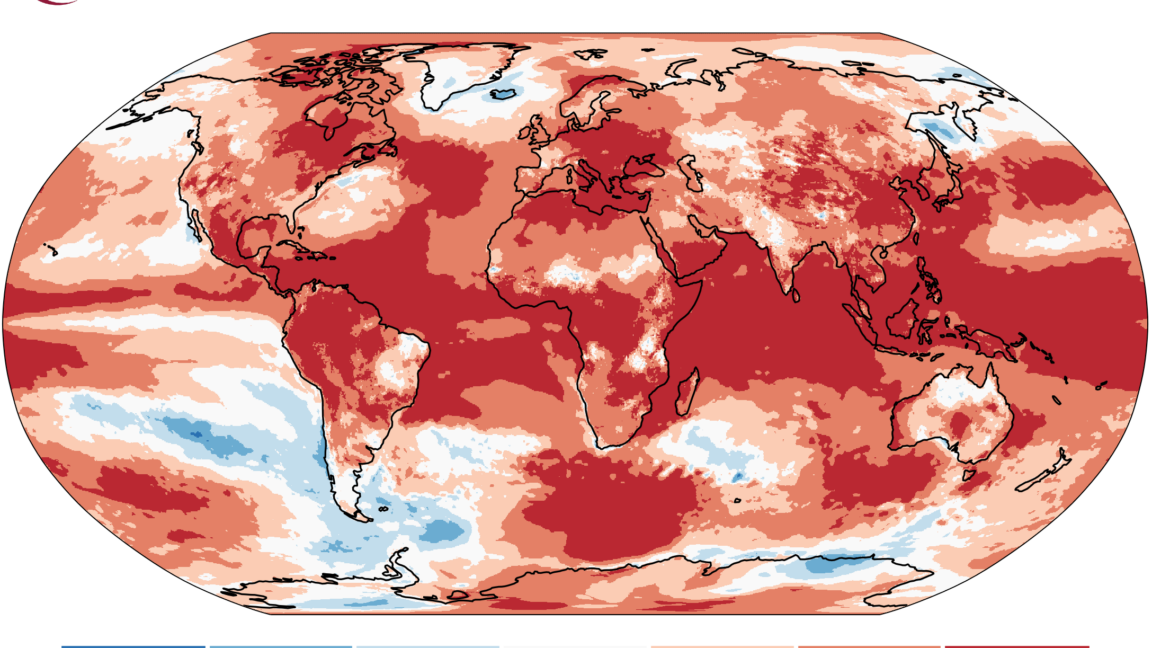








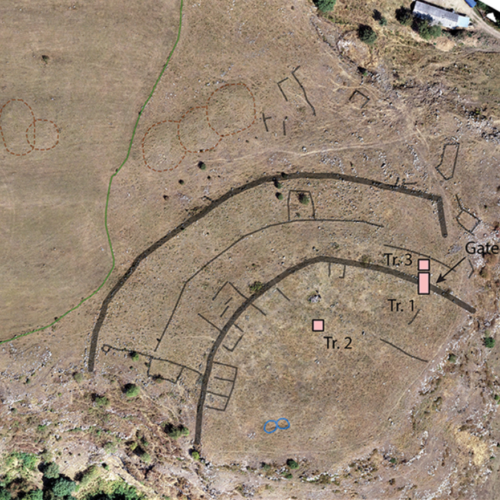
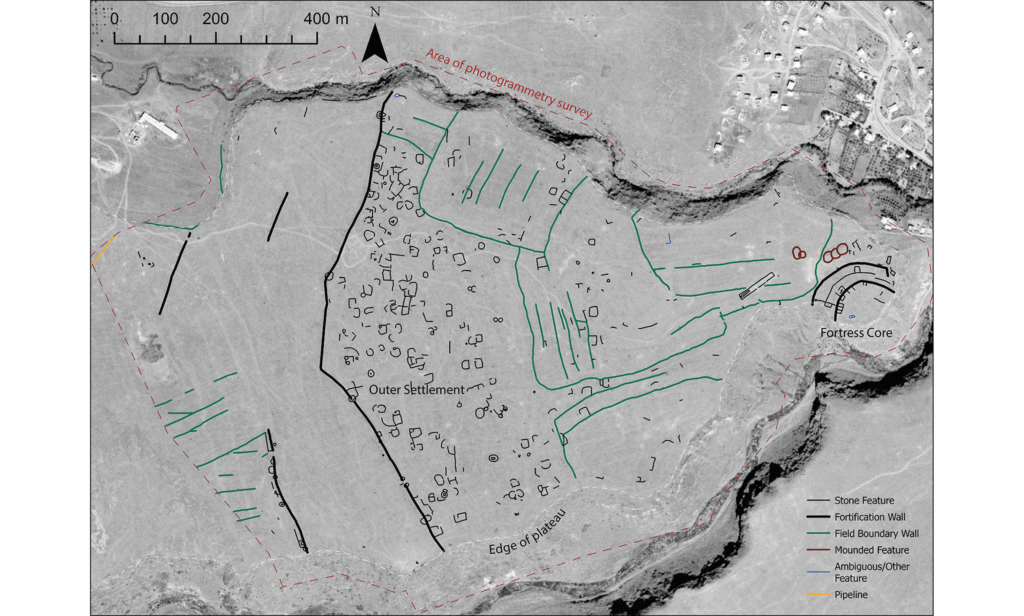 This map shows an aerial map of the ancient megafortress at Dmanisis Gora.
Credit:
Erb-Satullo et al. 2025
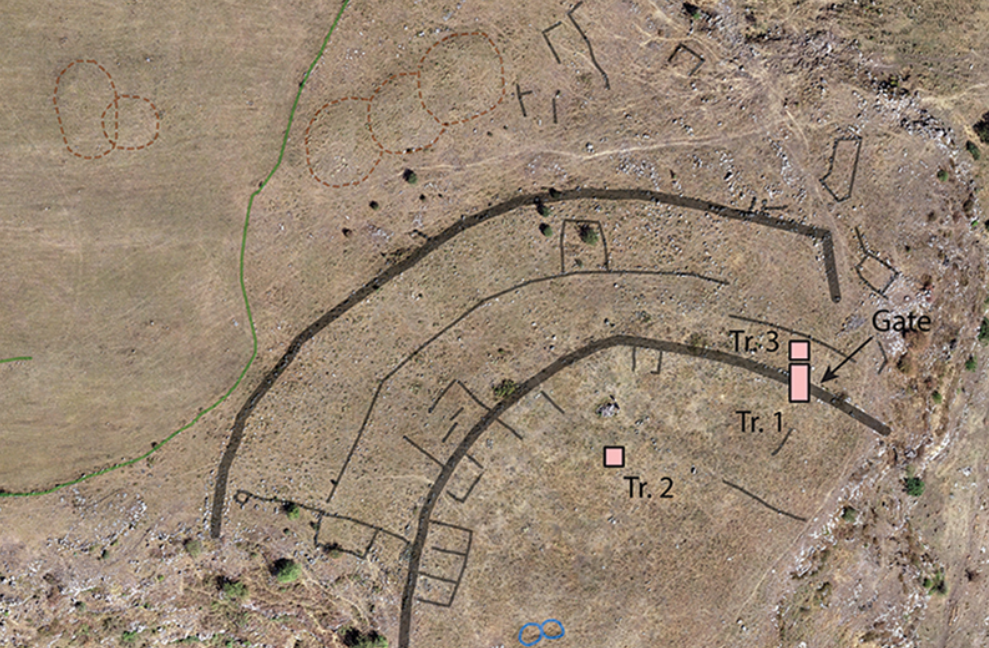
This map shows an aerial map of the ancient megafortress at Dmanisis Gora.
Credit:
Erb-Satullo et al. 2025